Python by itself is a strong Programming Language but if you want more than lines of codes and Grphical User Interface for users to interact with, you need a GUI framework.
PyQt is one of the GUI frameworks for Python Developers.
Qt by itself is a set of C++ libraries and tools. PyQt is Python binding to work with Qt.
Below is some of the guidelines installing PyQt5 on Debian Linux.
In some Linux Distros where you have two different versions of Python, 2.7 and 3, make sure you use Python3.
Python 2.7 is not officially supported past 2020 anyways so its a good idea to stick with Python3.
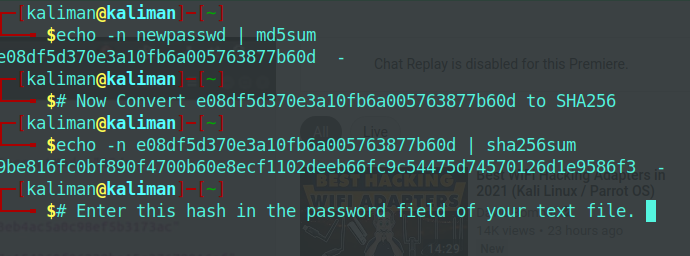
Check Python Version $python3 --version
it should show something like $python 3.7.3
if you are not already on Python 3.7, install the latest$sudo apt install python 3.7
Installation
$pip3 install --user pyqt5
$sudo apt-get install python3-pyqt5
$sudo apt-get install pyqt5-dev-tools
$sudo apt-get install qttools5-dev-tools
To test run, start by importing modules from PyQt5 –from PyQt5 import QtCore, QtGui, QtWidgets
Happy Coding
Regards
Teza